X-Ray vs. Gamma Ray Testing for Weld Inspection: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to non-destructive testing (NDT), few methods reveal as much detail as radiographic testing (RT). It lets inspectors “see” inside welds to locate porosity, inclusions, lack of fusion, or cracks that other techniques can miss.
Two RT methods dominate: X-ray and gamma ray testing. Both deliver internal images of welds, but each excels under different conditions. Understanding their differences helps technicians choose the right approach for each inspection—whether it’s a controlled shop weld or a remote pipeline joint.
Understanding the Basics
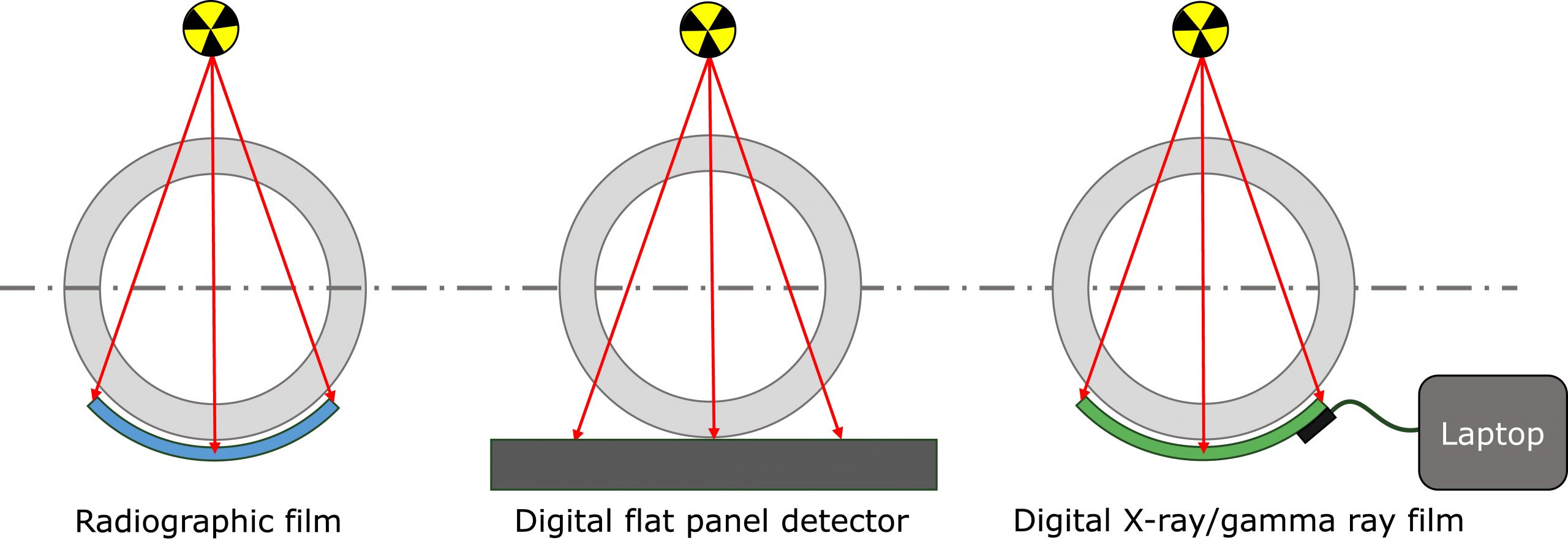
Radiography uses ionizing radiation to penetrate solid materials and create images of internal structures. The radiation passes through the weld and exposes a film or digital detector. Denser areas appear lighter or darker, revealing discontinuities.
The four main types of radiation are alpha, beta, gamma, and X-rays—but only X-rays and gamma rays have the energy needed for weld inspection. Gamma rays originate inside the atomic nucleus, while X-rays form outside it. Both can penetrate metal to produce high-contrast images.
When expanded to seven types (alpha, beta, gamma, X-rays, neutron, ultraviolet, and infrared), only gamma rays, X-rays, and neutrons are ionizing and used in NDT.
X-Ray Testing: Controlled Precision
X-rays are produced by high-voltage tubes that generate radiation on demand. Their energy can be adjusted, giving inspectors fine control over penetration and image clarity.
Common uses
Aerospace and structural welds
Manufacturing and fabrication inspections
Digital radiography (DR) applications for real-time results
Why inspectors choose X-ray/DR
Adjustable energy for better control
High image resolution for small-defect detection
Instant digital capture with no film development
Simplified storage, sharing, and documentation
Digital radiography (DR) advances X-ray inspection by replacing film with flat-panel detectors. DR eliminates darkroom processing, allows immediate image review, and improves workflow efficiency.
Gamma Ray Testing: Field-Ready and Powerful
Gamma rays come from radioactive isotopes such as Iridium-192 or Cobalt-60. Their energy levels are fixed by the isotope, but the beams penetrate much deeper than most X-rays.
Common uses
Pipeline welds
Thick steel components and vessels
Field inspections where power isn’t available
Advantages
Operates without electrical power
Compact, portable source containers
Excellent penetration through dense materials
Because gamma sources are self-contained, this method is ideal for remote field inspections and applications involving very thick materials that would require excessive X-ray power.
Film Radiography and Image Quality
Film radiography remains in use for applications that still require code compliance, such as pressure vessel and nuclear welds. Image quality depends on a sensitometric curve, which defines how film reacts to exposure.
Key terms
Optical density: The darkness of the image.
Gamma (slope) of the curve: Determines image contrast.
Proper calibration between source energy, exposure time, and film type ensures consistent, readable results. Many inspectors continue to rely on film where digital certification standards are still evolving.
X-Ray vs. Gamma Ray: Quick Comparison
| Feature | X-Ray | Gamma Ray |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Machine-generated (outside nucleus) | Radioactive isotope (inside nucleus) |
| Energy Control | Adjustable | Fixed by isotope |
| Penetration | Medium | High |
| Image Quality | High (especially with DR) | Moderate |
| Power Required | Yes | No |
| Best Use Case | Controlled environments | Field inspections |
Real-World Applications
Gamma in Action
Gamma radiography is widely used in pipeline and refinery inspections. A Cobalt-60 source can penetrate several inches of steel, making it suitable for heavy-wall components and remote field environments.
X-Ray with Digital Radiography
In contrast, X-ray with DR shines in controlled environments where clarity and workflow speed matter. Inspectors can view and validate results immediately, adjust exposure as needed, and make faster decisions—all while reducing radiation exposure and eliminating chemical waste.
How They Compare in Practice
X-Ray = Clarity and Control
Perfect for precision imaging, thin materials, and inspection sites with reliable power.
Gamma Ray = Power and Portability
Ideal for thick materials, deep penetration, and remote or confined sites.
Many teams now blend technologies—using gamma for penetration, DR for clarity, and UT or TOFD for defect sizing and verification. The right mix depends on code requirements, site conditions, and inspection goals.
Choosing the Right Method
When selecting between X-ray and gamma ray testing, consider:
Material type and thickness
Power availability
Required image detail and turnaround time
Applicable codes (API, ASME, AWS)
Safety, storage, and transport needs
Each method has its strengths. Together, they remain cornerstones of reliable weld inspection and quality assurance.
Final Takeaway: Clarity vs. Penetration
X-ray delivers clarity. Gamma delivers depth.
Understanding when to use each—and how digital radiography can complement both—helps NDT technicians achieve faster, safer, and more reliable weld evaluations in every industry.